How Technology in Sports is Innovating the Games We Play
Author: René Prüßner
Sports technology is becoming more advanced and widespread in recent years. From wearable devices to smart stadiums, it’s changing the way sports are played, coached, and enjoyed by fans.
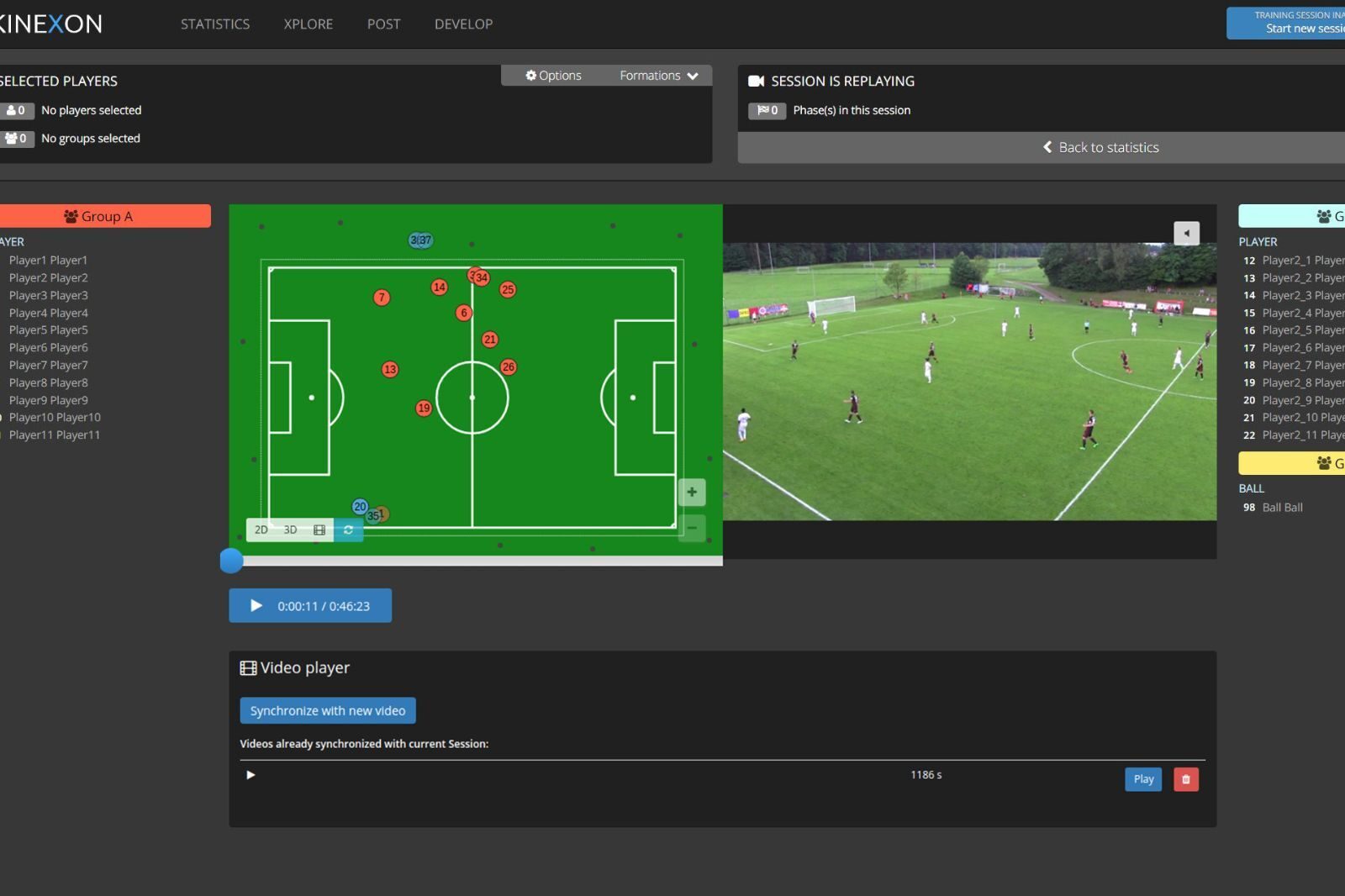
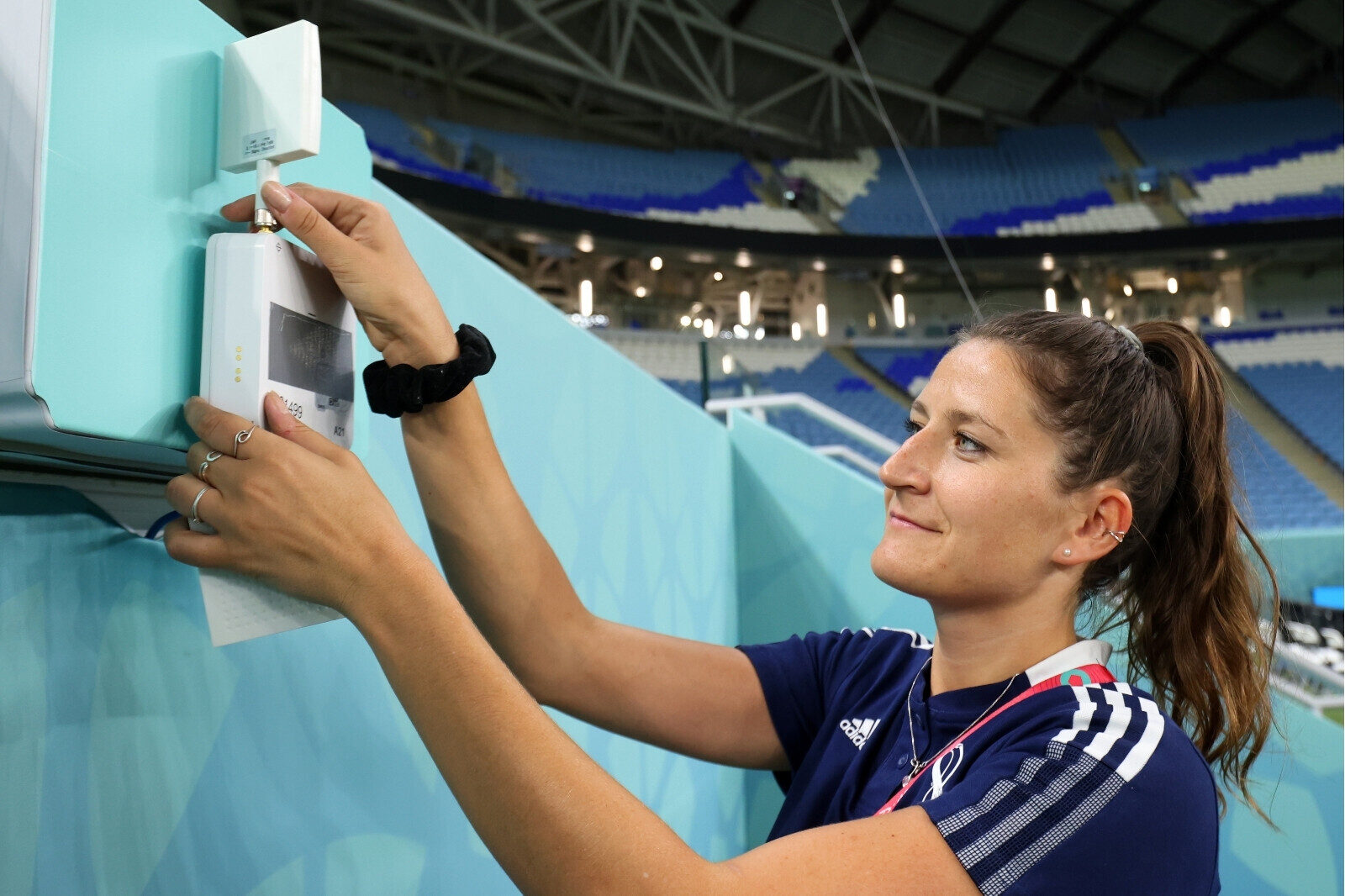
One of the most prominent examples of technology in sports is the use of tracking systems to measure and monitor the movements and performance of athletes. In this blog post, we will explore how three types of tracking systems — GPS, IMU, and LPS — are used by teams to track player metrics and gain a competitive edge.
What is GPS?

GPS stands for Global Positioning System, which is a satellite-based system that can determine the location and speed of an object on Earth.
GPS devices are commonly used in outdoor sports. GPS devices are usually worn by players in a vest, and they can transmit data wirelessly to a computer or a tablet.
What is IMU?

IMU stands for Inertial Measurement Unit, which is a device that can measure things like speed, acceleration, and workload of a player. It’s for indoor sports only like volleyball, basketball, and handball, but IMU systems are mobile, which means it can be used at home and on the road.
IMU devices are often integrated with LPS devices to provide more accurate and detailed data on the movements of players.
What is LPS?

LPS stands for Local Positioning System, which is a system that uses a locally deployed infrastructure, so called anchors, to determine the location and speed of a player within a defined area. The data is collected by wearables that are in a vest or the waistbands of the players’ shorts. It’s also very reliable.
LPS devices can also track the position and movement of the ball, which can provide valuable insights into the tactical aspects of the game.
Download our 4‑step guide to managing player workloads- both men and women.
How are GPS, IMU, and LPS used by teams?

Tracking systems can provide teams with a wealth of data that can be used for various purposes, such as:
- Describing the physical demands and characteristics of the sport, such as the average and peak speed, distance, and intensity of players, as well as the volume and duration of high-intensity actions, such as sprints, accelerations, and decelerations.
- Planning and monitoring the training load and the recovery of players, by using metrics such as the total distance, the high-speed distance, and metabolic power can help optimize the performance and prevent injuries of players.
- Evaluating the performance and the effectiveness of players can help identify the strengths and weaknesses of players and teams.
- Supporting the decision-making and the strategy of coaches, by using metrics such as the spatial distribution, the formation, the positioning, and the movement patterns of players and teams, as well as the interactions and the correlations between them, which can help improve the tactical and technical aspects of the game.
Benefits of Using Player Tracking Systems

- Providing objective and quantifiable data that can complement the subjective and qualitative observations of coaches and analysts.
- Enhancing feedback and communication between coaches and players, by using visual and interactive tools, such as dashboards, graphs, and heat maps, to illustrate and explain the data.
- Increasing the motivation and the engagement of players, by using gamification and personalization elements, such as goals, rewards, and rankings, to challenge and inspire players.
- Improving the fan experience and the media coverage, by using data visualization and storytelling techniques, such as live statistics, highlights, and narratives, to enrich and entertain the audience.
Sports Technology is Here to Stay

Sports tech is changing the games we play in many ways, and tracking systems are one of the most prominent examples of this trend.
By using GPS, IMU, and LPS devices, teams can track and analyze the movements and performance of players, and use the data to optimize their training, evaluation, decision-making, and strategy. However, tracking systems also require teams to be critical and careful in selecting, integrating, interpreting, and applying the data, as well as to be aware of the benefits and challenges that they entail.
That’s why you need a strong team behind your team when it comes to tracking player metrics and using the data.
If you’d like to learn more, check out our case study about a women’s handball team in the Netherlands that used sports tech to uncover misperceptions and manage their players better.














